Προγεννητικές εξετάσεις προσυμπτωματικού ελέγχου
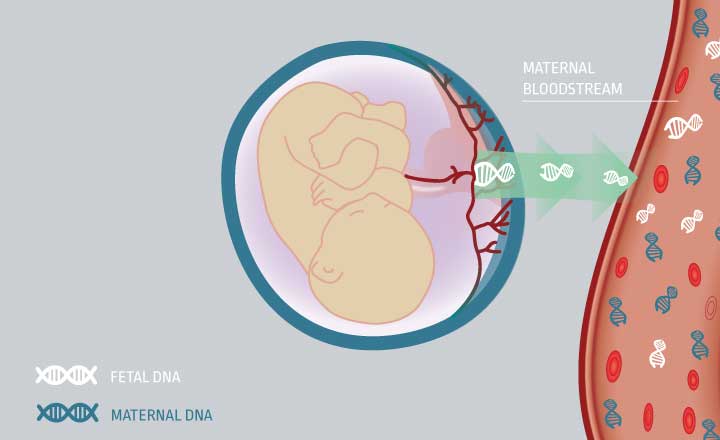
Τα τεστ προγεννητικού ελέγχου έχουν σχεδιαστεί για να σας παρέχουν πληροφορίες σχετικά με τη γενετική υγεία του μωρού σας. Με την καλύτερη κατανόηση των επιλογών προσυμπτωματικού ελέγχου, μπορείτε να πάρετε μια σίγουρη απόφαση σχετικά με το ποιο τεστ είναι καλύτερο για εσάς. Ο γυναικολόγος σας θα σας δώσει πρόσθετες πληροφορίες σχετικά με τις επιλογές εξέτασης.
Οι προγεννητικές εξετάσεις ελέγχου:
- Αξιολογούν τον κίνδυνο για ορισμένες συνθήκες στην κύηση
- Είναι ασφαλείς για την κύηση
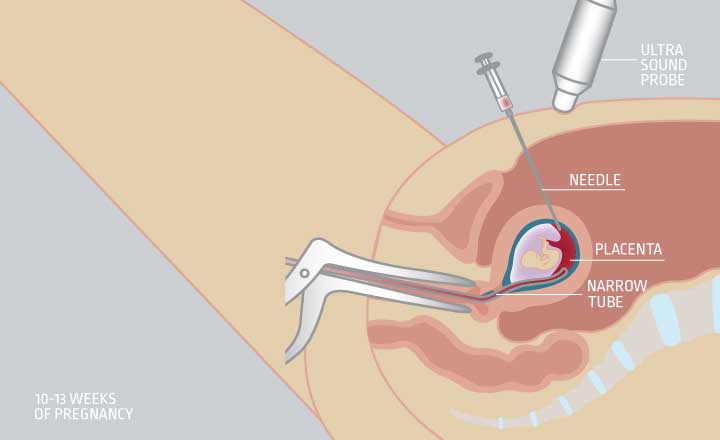
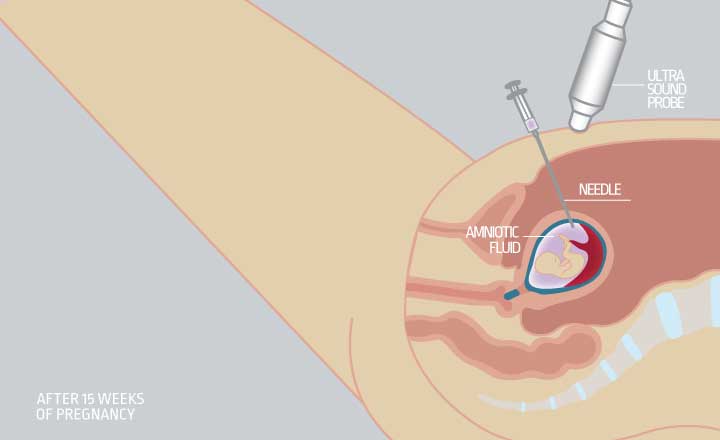
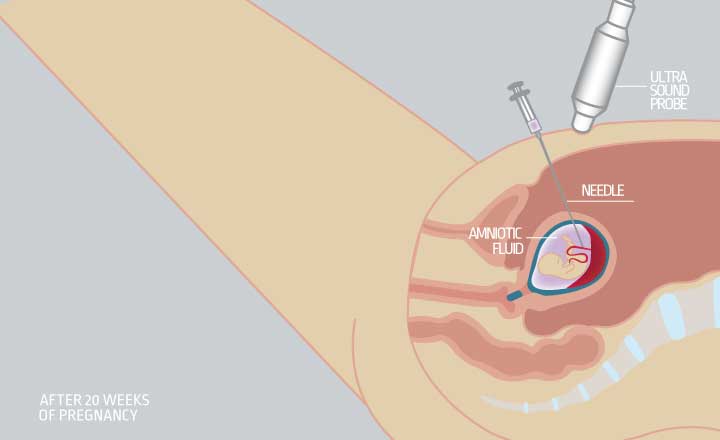
- Ακολουθούνται από πρόσθετες εξετάσεις, εφόσον χρειάζεται διάγνωση
- Μπορούν να πραγματοποιηθούν ήδη από τη 10η εβδομάδα της κύησης