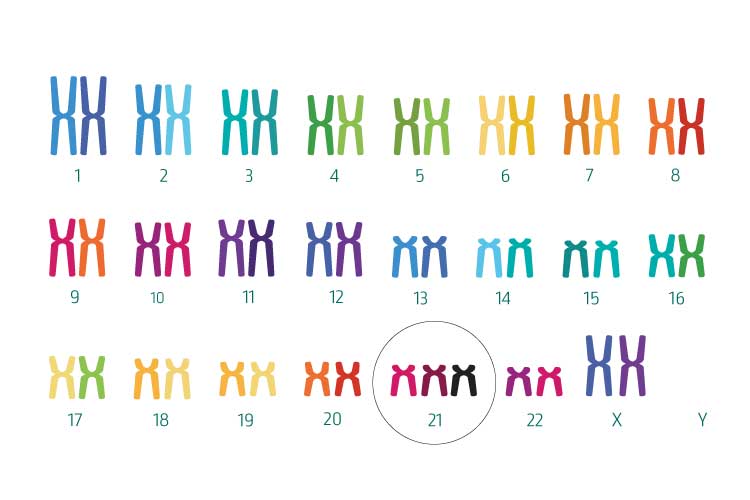
Τρισωμία 21 (σύνδρομο Down)
Η τρισωμία 21 προκαλείται από την παρουσία ενός επιπλέον αντιγράφου του χρωμοσώματος 21 και είναι η πιο κοινή μορφή χρωμοσωμικής διαταραχής στους ανθρώπους. Αυτή η τρισωμία οδηγεί στο σύνδρομο Down, το οποίο σχετίζεται με γενικά μέτρια διανοητική αναπηρία και άλλες διαταραχές, όπως οι συγγενείς καρδιοπάθειες. Η τρισωμία 21 εμφανίζεται σε 1 στις 500 εγκυμοσύνες. Περίπου το ένα τρίτο των κυήσεων με τρισωμία 21 καταλήγουν σε αποβολή. Επομένως, υπολογίζεται ότι μόνο 1 στα 830 νεογνά προσβάλλεται από τρισωμία 21. Η πιθανότητα τρισωμίας 21 σχετίζεται σε μεγάλο βαθμό με την ηλικία της μητέρας. Για παράδειγμα, ο κίνδυνος για τρισωμία 21 σε μια 20χρονη έγκυο γυναίκα είναι κατά μέσο όρο 1 στις 1.050, ενώ ο κίνδυνος σε μια έγκυο 40 ετών είναι περίπου 1 στις 100 (πληροφορίες από το τέλος του πρώτου τριμήνου ).